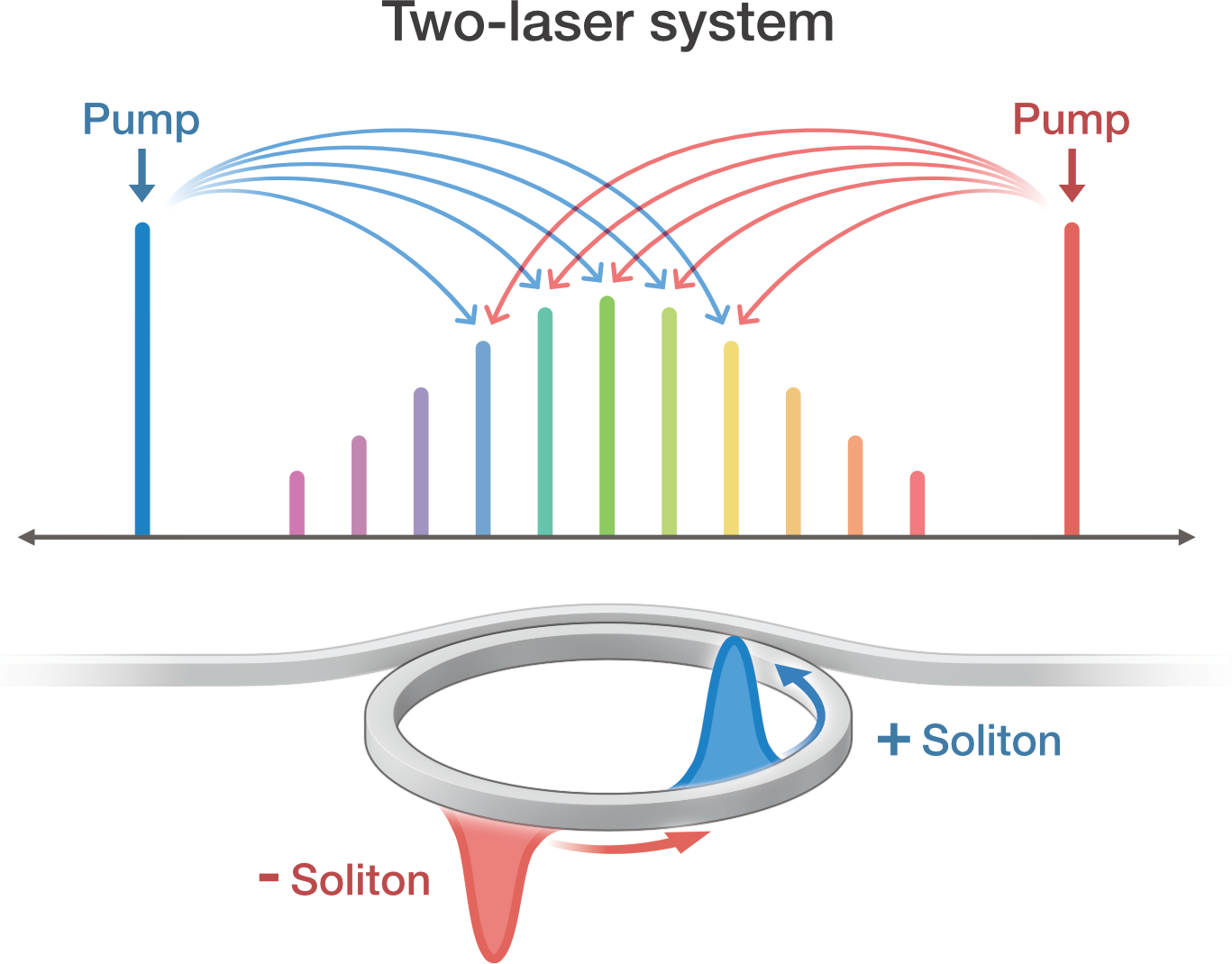
Together with colleagues from the University of Auckland, Universite libre de Bruxelles, and Universite de Bourgogne, we have investigated a new type of microresonator soliton frequency comb, called a parametrically driven, pure-Kerr soliton comb, as reported in a recent issue of Nature Photonics. These new soliton combs are driven by a pair of pump lasers, and are spectrally located in between the two lasers. The fundamental differences in how they are driven in comparison to typical singly-pumped Kerr cavity solitons lead to a number of interesting properties. For example, the soliton pulses come in two different flavors with opposite phases, and the noise properties of the generated comb teeth are expected to be different.
More information can be found in press releases from NIST and JQI.