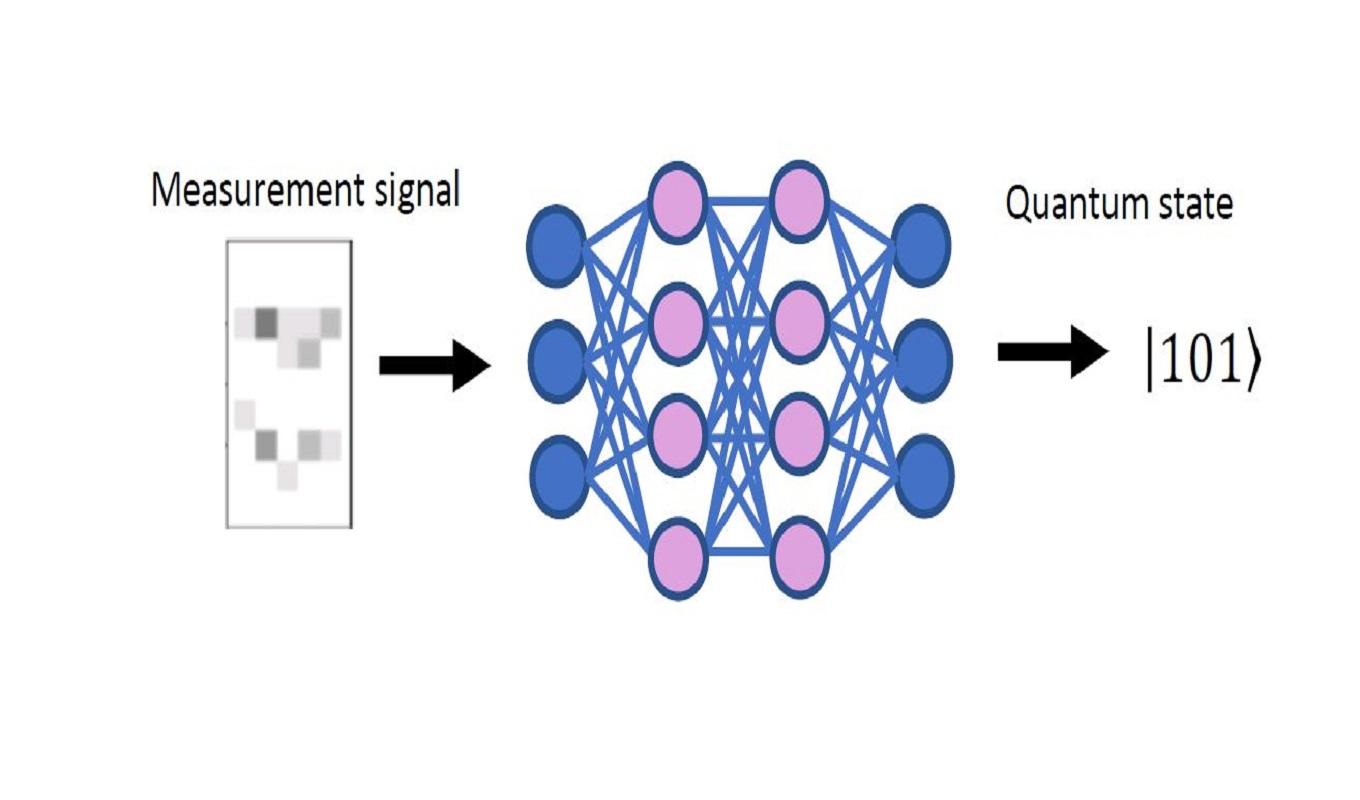
We reduce measurement errors in a quantum computer using machine learning techniques. We exploit a simple yet versatile neural network to classify multi-qubit quantum states, which is trained using experimental data. This flexible approach allows the incorporation of any number of features of the data with minimal modifications to the underlying network architecture. We experimentally illustrate this approach in the readout of trapped-ion qubits using additional spatial and temporal features in the data. Using this neural network classifier, we efficiently treat qubit readout crosstalk, resulting in a 30% improvement in detection error over the conventional threshold method. Our approach does not depend on the specific details of the system and can be readily generalized to other quantum computing platforms.