Epitaxial InAs/GaAs quantum dots are well-established as the basis for bright single-photon sources, because they have nearly unity radiative efficiency and can be emebdded in photonic geometries that enable efficient funneling of the generated photons into a preferred optical channel.
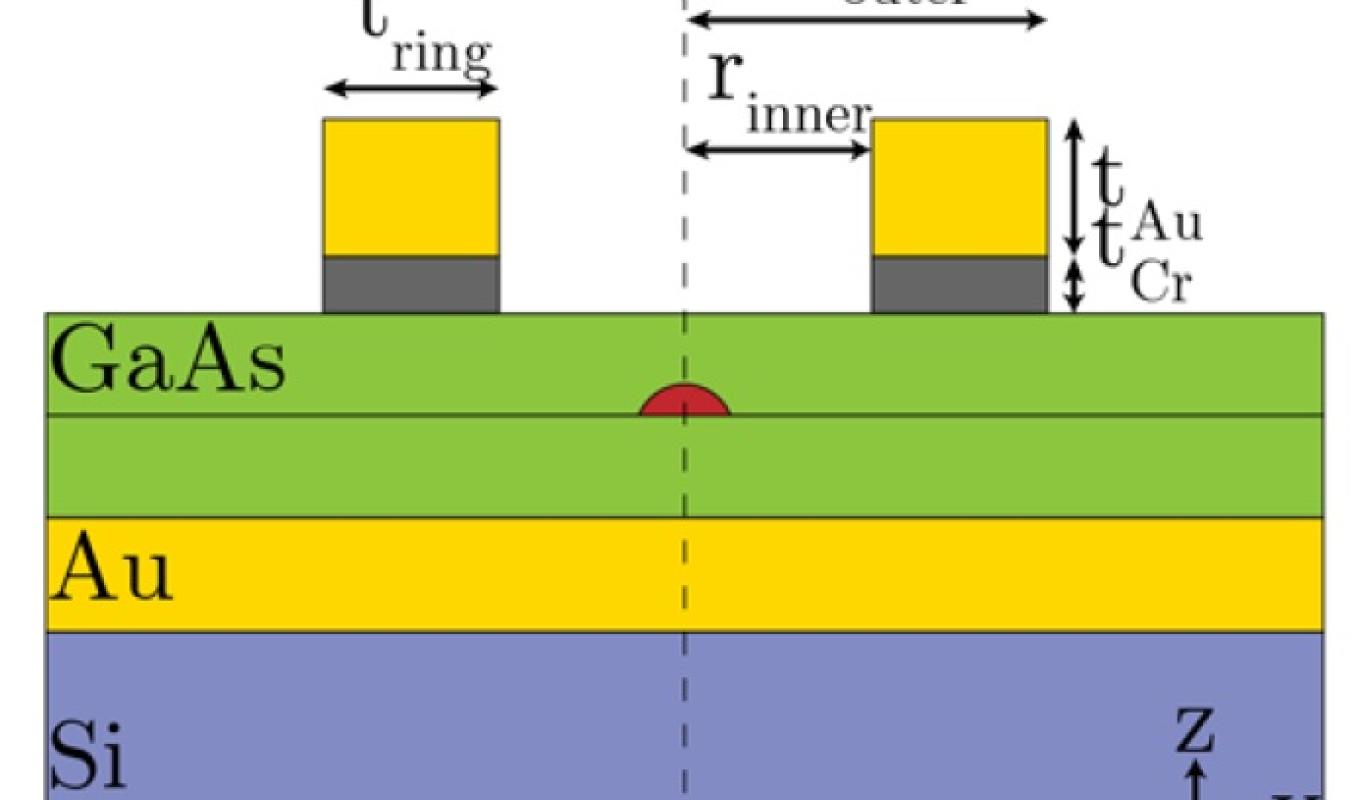
In a recent work led by our collaborators Cori Haws and Luca Sapienza at the University of Glasgow (and visiting researchers at NIST), we explore a spectrally broadband approach for the photonic geometry, consisting of a metallic nanoring placed above the top surface of the quantum dot containing material, and a planar gold mirror deposited on the underlying surface. This approach provides broadband enhancement of the emission across the full spectral range over which an ensemble of such quantum dots emits. Moreoever, it does not require any etching of nanostructures in proximity of the quantum dots, which is known to lead to adverse quantum dot behavior due to interaction with surface states. We anticipate that this approach can be a valuable way to enhance light emission from quantum dots for a variety of purposes, including basic studies of quantum dot behavior.
Haws, C., E. Perez, M. Davanço, J. Dong Song, K. Srinivasan, and L. Sapienza, "Broadband, efficient extraction of quantum light by a photonic device comprised of a metallic nano-ring and a gold back reflector", Appl. Phys. Lett., vol. 120, pp. 081103, 2022.