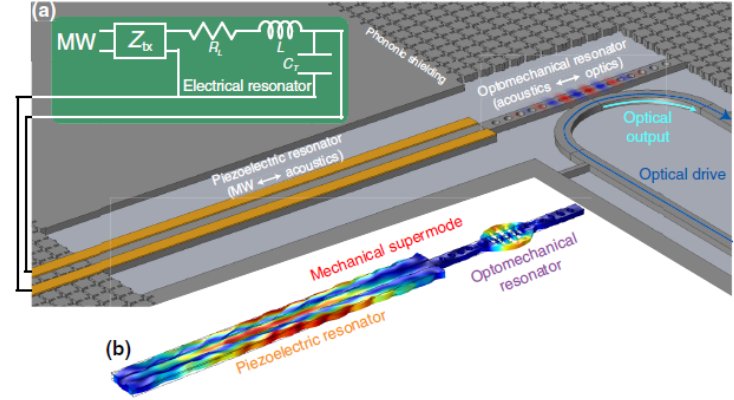
Proposed microwave-to-optical transducer using piezo-optomechanics (Wu et al, Phys Rev Appl, 2020).
Two results on microwave-to-optical transduction using piezo-optomechanical devices have recently been published:
- In Physical Review Applied, we propose and analyze a scheme for efficient and low-noise transduction using coupled piezoelectric and optomechanical resonators (https://journals.aps.org/prapplied/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevApplied.13.014027). This work give us a blueprint for future experimental development across a number of materials platforms.
- In Nature Physics, our collaborators from Simon Groblacher's group at TU Delft have measured microwave-to-optical transducers operating in the quantum ground state (https://www.nature.com/articles/s41567-019-0673-7). The elimination of thermomechanical noise in piezo-optomechanical devices has also been studied by our collaborators in John Davis's group at the University of Alberta in a recent paper in Physical Review Letters (https://journals.aps.org/prl/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevLett.123.093603). The initial design and room-temperature characterization of piezo-optomechanical transducers that coherently couple microwaves, acoustic waves, and optical waves was reported earlier by our group in Nature Photonics (https://www.nature.com/articles/nphoton.2016.46).
TEMP migration NID
1761