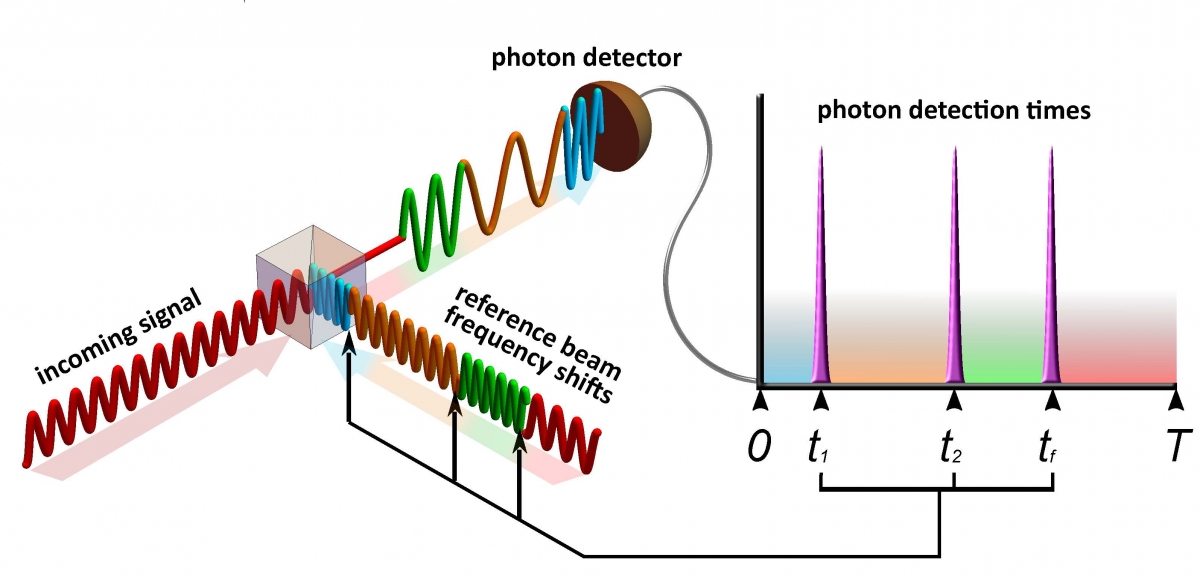
The incoming signal (red, lower left) proceeds through a beam splitter to the photon detector, which has an attached time register (top right). The receiver sends the reference beam to the beam splitter to cancel the incoming pulse so that no light is detected. If even one photon is detected, it means that the receiver used an incorrect reference beam, which needs to be adjusted. The receiver uses exact times of photon detection to arrive at the right adjustment with fewer guesses. The combination of recorded detection times and the history of reference beam frequencies are used to find the frequency of the incoming signal. (Credit: NIST)
Researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), the Department of Physics at the University of Maryland (UMD) and JQI have devised and demonstrated a system that could dramatically increase the performance of communications networks while enabling record-low error rates in detecting even the faintest of signals. The work could potentially decrease the total amount of energy required for state-of-the-art networks by a factor of 10 to 100.
The proof-of-principle system consists of a novel receiver and corresponding signal-processing technique that, unlike the methods used in today’s networks, are entirely based on the properties of quantum physics and thereby capable of handling even extremely weak signals with pulses that carry many bits of data.
“We built the communication test bed using off-the-shelf components to demonstrate that quantum-measurement-enabled communication can potentially be scaled up for widespread commercial use,” said Ivan Burenkov, a research scientist at JQI. Burenkov and his colleagues report the results in Physical Review X Quantum. “Our effort shows that quantum measurements offer valuable, heretofore unforeseen advantages for telecommunications leading to revolutionary improvements in channel bandwidth and energy efficiency.”
Modern communications systems work by converting information into a laser-generated stream of digital light pulses in which information is encoded—in the form of changes to the properties of the light waves—for transfer and then decoded when it reaches the receiver. The train of pulses grows fainter as it travels along transmission channels, and conventional electronic technology for receiving and decoding data has reached the limit of its ability to precisely detect the information in such attenuated signals.
The signal pulse can dwindle until it is as weak as a few photons—or even less than one on average. At that point, inevitable random quantum fluctuations called “shot noise” make accurate reception impossible by normal (“classical,” as opposed to quantum) technology because the uncertainty caused by the noise makes up such a large part of the diminished signal. As a result, existing systems must amplify the signals repeatedly along the transmission line, at considerable energy cost, keeping them strong enough to detect reliably.
The NIST team’s system can eliminate the need for amplifiers because it can reliably process even extremely feeble signal pulses: “The total energy required to transmit one bit becomes a fundamental factor hindering the development of networks,” said Sergey Polyakov, senior scientist on the NIST team and an adjunct associate professor of physics at UMD. “The goal is to reduce the sum of energy required by lasers, amplifiers, detectors, and support equipment to reliably transmit information over longer distances. In our work here we demonstrated that with the help of quantum measurement even faint laser pulses can be used to communicate multiple bits of information—a necessary step towards this goal.”
To increase the rate at which information can be transmitted, network researchers are finding ways to encode more information per pulse by using additional properties of the light wave. So a single laser light pulse, depending on how it was originally prepared for transmission, can carry multiple bits of data. To improve detection accuracy, quantum-enhanced receivers can be fitted onto classical network systems. To date, those hybrid combinations can process up to two bits per pulse. The NIST quantum system uses up to 16 distinct laser pulses to encode as many as four bits.
To demonstrate that capability, the NIST researchers created an input of faint laser pulses comparable to a substantially attenuated conventional network signal, with the average number of photons per pulse from 0.5 to 20 (though photons are whole particles, a number less than one simply means that some pulses contain no photons).
After preparing this input signal, the NIST researchers take advantage of its wavelike properties, such as interference, until it finally hits the detector as photons (particles). In the realm of quantum physics, light can act as either particles (photons) or waves, with properties such as frequency and phase (the relative positions of the wave peaks).
Inside the receiver, the input signal’s pulse train combines (interferes) with a separate, adjustable reference laser beam, which controls the frequency and phase of the combined light stream. It is extremely difficult to read the different encoded states in such a faint signal. So the NIST system is designed to measure the properties of the whole signal pulse by trying to match the properties of the reference laser to it exactly. The researchers achieve this through a series of successive measurements of the signal, each of which increases the probability of an accurate match.
That is done by adjusting the frequency and phase of the reference pulse so that it interferes destructively with the signal when they are combined at the beam splitter, canceling the signal out completely so no photons can be detected. In this scheme, shot noise is not a factor: Total cancellation has no uncertainty.
Thus, counterintuitively, a perfectly accurate measurement results in no photon reaching the detector. If the reference pulse has the wrong frequency, a photon can reach the detector. The receiver uses the time of that photon detection to predict the most probable signal frequency and adjusts the frequency of the reference pulse accordingly. If that prediction is still incorrect, the detection time of the next photon results in a more accurate prediction based on both photon detection times, and so on.
“Once the signal interacts with the reference beam, the probability of detecting a photon varies in time,” Burenkov said, “and consequently the photon detection times contain information about the input state. We use that information to maximize the chance to guess correctly after the very first photon detection.
“Our communication protocol is designed to give different temporal profiles for different combinations of the signal and reference light. Then the detection time can be used to distinguish between the input states with some certainty. The certainty can be quite low at the beginning, but it is improved throughout the measurement. We want to switch the reference pulse to the right state after the very first photon detection because the signal contains just a few photons, and the longer we measure the signal with the correct reference, the better our confidence in the result is.”
Polyakov discussed the possible applications. “The future exponential growth of the internet will require a paradigm shift in the technology behind communications,” he said. “Quantum measurement could become this new technology. We demonstrated record low error rates with a new quantum receiver paired with the optimal encoding protocol. Our approach could significantly reduce energy for telecommunications.”
This story was originally published by NIST News. It has been adapted with minor changes here. JQI is a research partnership between UMD and NIST, with the support and participation of the Laboratory for Physical Sciences.